Magnetic Flux Structures In Superconductors: Unraveling the Secrets of Superconductivity

Superconductivity, the ability of certain materials to conduct electricity without resistance, is a remarkable phenomenon that has captivated scientists and engineers for over a century. At the heart of superconductivity lies the formation of magnetic flux structures, which play a pivotal role in determining the material's superconducting properties.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8594 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 300 pages |
Magnetic Flux Structures and Superconductivity
When a superconductor is exposed to an external magnetic field, magnetic flux penetrates the material in the form of quantized units called flux quanta. These flux quanta organize themselves into distinct structures, known as magnetic flux structures, which can vary in shape and size depending on the material and the applied magnetic field.
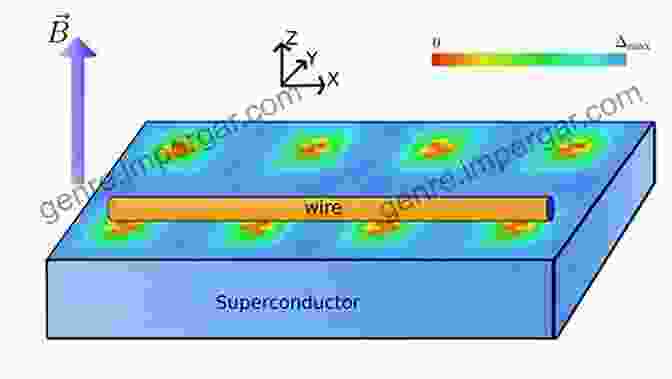
The most common type of magnetic flux structure is the vortex, which consists of a central core of normal material surrounded by a circulating supercurrent. Vortices can form when the applied magnetic field exceeds a critical value, known as the critical magnetic field.
Abrikosov Lattice
In type-II superconductors, vortices arrange themselves into a regular hexagonal lattice called the Abrikosov lattice. This lattice structure minimizes the energy of the superconducting state and provides a stable configuration for the magnetic flux. The spacing of the vortices in the Abrikosov lattice is determined by the applied magnetic field and the material's properties.
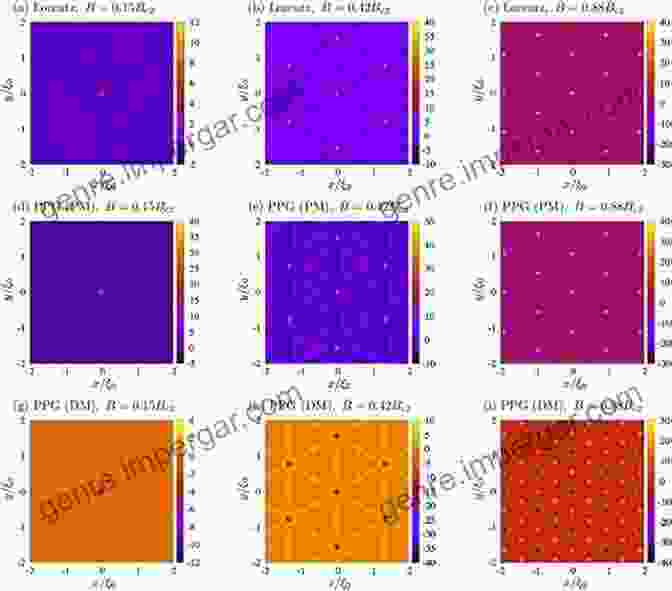
Critical Magnetic Field and Critical Current
The critical magnetic field is a key parameter in superconductivity. It represents the maximum magnetic field that can be applied to a superconductor without destroying the superconducting state. Beyond the critical magnetic field, the superconductor undergoes a transition to the normal state, where it exhibits electrical resistance.
Closely related to the critical magnetic field is the critical current. This is the maximum current that can flow through a superconductor without causing it to transition to the normal state. The critical current is determined by the strength of the magnetic field and the material's properties.
Flux Pinning and Flux Creep
In practical applications, it is often desirable to enhance the critical magnetic field and critical current of superconductors. This can be achieved through flux pinning, a process where defects or inclusions in the material act as pinning centers for the vortices. By pinning the vortices, their motion is restricted, which helps to maintain the superconducting state in the presence of higher magnetic fields and currents.
However, over time, vortices can overcome the pinning forces and move through the material, a process known as flux creep. Flux creep can lead to a decrease in the critical current and a degradation of the superconducting properties.
Josephson Effect and SQUIDs
Magnetic flux structures play a crucial role in the Josephson effect, which is a phenomenon that occurs when two superconductors are separated by a thin insulating layer. When a voltage is applied across the junction, a supercurrent flows between the superconductors, mediated by the exchange of Cooper pairs, which are pairs of electrons that carry the superconducting current.
One practical application of the Josephson effect is the development of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices). SQUIDs are highly sensitive magnetometers that utilize the Josephson effect to measure extremely small magnetic fields. They have applications in various fields, including medical imaging, geophysics, and particle physics.
Magnetic Levitation
Magnetic flux structures are also responsible for the phenomenon of magnetic levitation, where objects can be suspended in the air without physical contact. By creating a strong magnetic field gradient, magnetic flux structures can induce a repulsive force that levitates the object against the force of gravity.
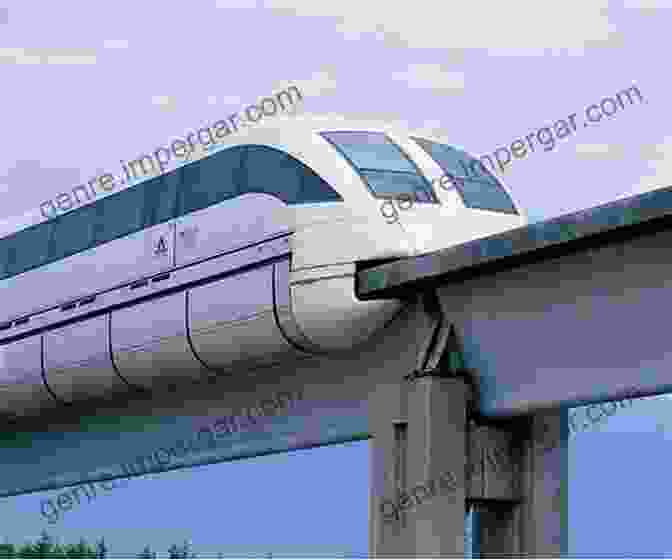

Magnetic levitation has practical applications in high-speed transportation systems, such as maglev trains, which can travel at speeds of over 300 miles per hour due to the absence of mechanical friction.
Magnetic flux structures are fascinating and complex phenomena that lie at the heart of superconductivity. Their understanding and manipulation have led to the development of groundbreaking technologies, including SQUIDs, magnetic levitation systems, and high-performance superconductors with applications in diverse fields.
As research in superconductivity continues to advance, we can expect even more remarkable discoveries and innovations that harness the power of magnetic flux structures to shape the future of technology.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8594 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 300 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia T Tinga
T Tinga Liesbeth Heenk
Liesbeth Heenk Peter A Ziegler
Peter A Ziegler Mark Puls
Mark Puls Tracy B Strong
Tracy B Strong Marcel Proust
Marcel Proust Lynford Graham
Lynford Graham Luis E Navia
Luis E Navia Simon Morden
Simon Morden Lisa Rusczyk
Lisa Rusczyk Lidia Zylowska
Lidia Zylowska Peter Beater
Peter Beater Maliek Blade
Maliek Blade Vanessa Williams
Vanessa Williams Mara Schiavocampo
Mara Schiavocampo Marc Heller
Marc Heller Sonya Judd
Sonya Judd Loutfy H Madkour
Loutfy H Madkour Ludwig Weber
Ludwig Weber Peter L Privalov
Peter L Privalov
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Andres CarterActivities Funded By The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Trust Fund Gao...
Andres CarterActivities Funded By The Patient Centered Outcomes Research Trust Fund Gao...
 Dominic SimmonsSpirituality Evolution And Awakened Consciousness: The Ultimate Guide to...
Dominic SimmonsSpirituality Evolution And Awakened Consciousness: The Ultimate Guide to... Jack LondonFollow ·8.7k
Jack LondonFollow ·8.7k Jace MitchellFollow ·5.2k
Jace MitchellFollow ·5.2k Quentin PowellFollow ·15.7k
Quentin PowellFollow ·15.7k Glen PowellFollow ·2.6k
Glen PowellFollow ·2.6k Alan TurnerFollow ·9.2k
Alan TurnerFollow ·9.2k Kyle PowellFollow ·2.4k
Kyle PowellFollow ·2.4k H.G. WellsFollow ·16.1k
H.G. WellsFollow ·16.1k Mario BenedettiFollow ·10.9k
Mario BenedettiFollow ·10.9k

 J.D. Salinger
J.D. SalingerThe Montefeltro Conspiracy Renaissance Mystery Decoded
In the heart of the Italian Renaissance, a...

 Ryūnosuke Akutagawa
Ryūnosuke AkutagawaElan Vital Magazine: A Literary Sanctuary for the Mind...
In this fast-paced digital age, where...

 Derek Bell
Derek BellCode Biology: Unveiling the New Science of Life
Every living organism, from...

 Rick Nelson
Rick NelsonUnleash the Darkness: Dive into the World of Villain Arts...
Prepare to be...

 Tony Carter
Tony CarterEmbark on a Scientific Odyssey: Unveil the Secrets of...
In an era where environmental concerns...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8594 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 300 pages |